1. Vector calculus
: Vector calculus는 algorithms of control과 machine learning에서 아주 중요한 역할을 한다.
: Finding good variables or parameters can be phrased as an optimization problem.
Examples
1] Linear regression where we look at curve-fitting problems and optimize linear weight parameters to maximize the likelihood.
2] Neural-network auto enders for dimensionality reduction and data compression, where the parameters are the weights and biases of each layer, and where we minimize a reconstruction error by repeated application of the chain-rule.
3] Gaussian mixture models for modeling data distributions where we optimize the location and shape parameters of each mixture component to maximize the likelihood of the model.
=> 대부분 자연스럽게 익히게된다!
=> 참고하려면 아래의 링크로
http://www.kocw.net/home/search/kemView.do?kemId=1232254
벡터미적분학(벡터필드)
제공처: 뉴 사우스 웨일즈 대학
www.kocw.net
1) Function
-> A function \( f \) is a quantity that relates two quantities to each other.
We often write
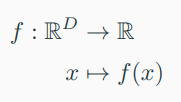
to specify a function. Here \( R^{D} \) is the domain (정의역) , \( f \) and the function values \( f \) are the image/codomain(공역) of \( f \).
* Range : 치역
2) Difference quotient
-> We start with the difference quotient (몫) of a univariate function \(y = f(x)\) which we will subsequently use to define derivatives.
* univariate function : A function of a single variable.
-> Definition (Difference Quotient)
The difference quotient
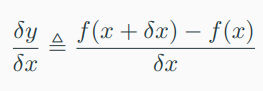
-> 두 점의 secant (할선, 교차하는) line (기울기랑 동일)
3) Derivative
-> For \(h > 0\) the derivative of \(f\) at \(x\) is defined as the limit
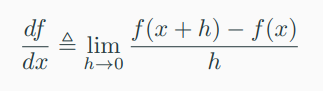
-> 이 때 앞선 secant line은 tangent가 된다.
-> The derivative of \(f\) points in the direction of steepest ascent of \(f\).
4) Taylor series
-> \(f\)를 an infinite sum of terms로 표현한다.
-> 해당 terms들은 \(f\)의 derivatives (evaluated at \(x_0 \) )를 사용하여 결정된다.
-> The Taylor polynominal of degree \(n\) of \(f\) : \( R \rightarrow R \) at \( x_{0} \) is defined as
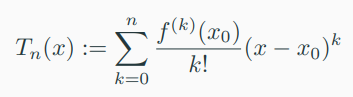
-> where \( f^{(k)}(x_{0}) \) is the \(k\) derivative of \(f\) at \( x_{0} \) (which we assume exists) and \( \frac{f^{(k)}(x_{0})}{k!} \) are the coefficients of the polynomial.
-> Definition (Taylor Series)
: For a smooth function \( f \in C^{\infty} \), 나머지는 위와 동일, is defined as
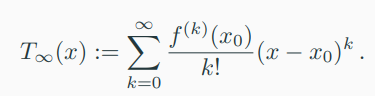
-> For \(x_{0}\), we obtain the Maclaurin series as a special instance of the Taylor series. If \(f(x) = T_{\infty}(x)\) then \(f\) is called \(analytic\).
5) Differentiation rules
1] 기본적인 differentiation rules
-> \( f \) by \( f' \)
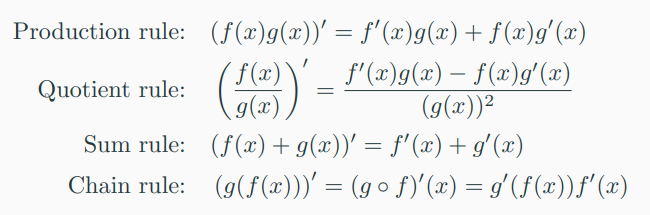
-> where \( g \circ f \) denotes function composition \( x \mapsto f(x) \mapsto g(f(x)) \)
2] 기본적인 partial differentiation
-> \( f \) 가 하나 또는 여러개의 변수 \( x \in R^n \)에 의존한다고 하자.
-> The generalization of the derivative to functions of several variables is the gradient.
-> Definition (Partial Derivative)
-> \( f : R^n \rightarrow R \) of \( x \in R^n \), the partial derivatives as

-> and collect them in the row vector.
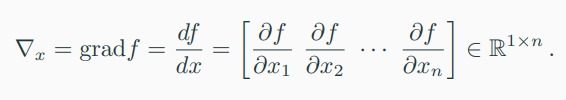
'Study > Reinforcement learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 강화학습_(5) - 머신 러닝 분류 - 지도 학습, 비지도 학습, 강화 학습 (0) | 2019.10.30 |
|---|---|
| 강화학습_(4) - Math Preliminary_2 (0) | 2019.10.23 |
| 강화학습_(3) - 시그모이드 (Sigmoid)함수 정의 (0) | 2019.10.21 |
| 강화학습_(2) - Python 기초_4 (0) | 2019.10.20 |
| 강화학습_(2) - Python 기초_3 (0) | 2019.10.20 |